What is Solar Cell?

What is Solar Cell?
Solar Cell or Photovoltaic (PV) cell is a device that is made up of semiconductor materials such as silicon, gallium arsenide and cadmium telluride, etc. that converts sunlight directly into electricity. When solar cells absorb sunlight, free electrons and holes are created at positive/negative junctions. If the positive and negative junctions of solar cell are connected to DC electrical equipment, current is delivered to operate the electrical equipment.
Solar cell types
There are three major cell types that classified by its manufacturing technology and the semiconductor:
1. Crystalline Silicon PV Module: Two types of crystalline silicon (c-Si) are used to produce PV module; single crystalline silicon or known as monocrystalline silicon and multi-crystalline silicon, also called polycrystalline silicon. The polycrystalline silicon PV module has lower conversion efficiency than single crystalline silicon PV module but both of them have high conversion efficiencies that average about 10-12%.
2. Amorphous Silicon PV Module: Amorphous silicon (a-Si) PV module or thin-film silicon PV module absorbs light more effectively than crystalline silicon PV module, so it can be made thinner. It suits for any applications that high efficiency is not required and low cost is important. The typical efficiency of amorphous silicon PV module is around 6%.
3. Hybrid Silicon PV Module: A combination of single crystalline silicon surrounded by thin layers of amorphous silicon provides excellent sensitivity to lower light levels or indirect light. The Hybrid silicon PV module has highest level of conversion efficiency about 17%.
How solar cell works?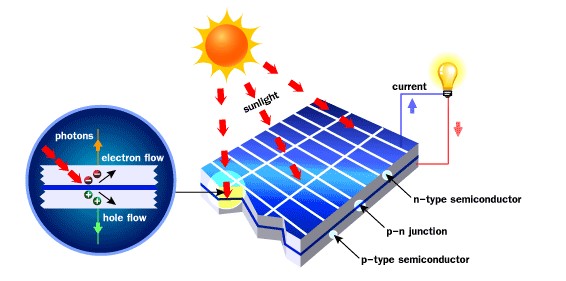
When sunlight strikes solar cell surface, the cell creates charge carrier as electrons and holes. The internal field produced by junction separates some of positive charges (holes) from negative charges (electrons). Holes are swept into positive or p-layer and electrons are swept into negative or n-layer. When a circuit is made, free electrons have to pass through the load to recombine with positive holes; current can be produced from the cells under illumination.
The individual solar cells are connected together to make a module (called solar panel or PV panel ) to increase current and the modules are connected in an array (called ‘solar array’ or ‘PV array’). Depending on current or voltage requirement, solar arrays are connected in a variety of ways: • If the solar arrays are connected in parallel, the output current will increase.
• If the solar arrays are connected in series, the output voltage will increase.
What is the advantage of solar cell?
Solar cell or PV cell produces clean with non-polluting energy source of electricity that is environmental-friendly. Since it uses no fuel other than sunlight, gives off no waste, no burning, and no moving part when it operates. It reduces collection of gases such as carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrocarbon and nitrogen, etc., which generated from fuel, coal and fossil fuel burning power plants. All decrease the impacts of energy on the environment like greenhouse effect, global warming, acid rain and air pollution, etc. It is easy to install and transportable. With the modular characteristic, it can be constructed any sizes as required. Moreover, it requires minimal maintenance and has long life span (more than 30 years) and stable efficiency.
What is the application of solar cell?
1) Home Indoor and outdoor lighting system, electrical equipment, electric gate opener, security system, ventilator, water pump, water filter and emergency light, etc.
2) Lighting system Bus stop lighting, telephone booth lighting, billboard lighting, parking lot lighting, indoor and outdoor lighting and street lighting, etc.
3) Water pumping Consumption, public utility, livestock watering, agriculture, gardening and farming, mining and irrigation, etc.
4) Battery charging system Emergency power system, battery charging center for rural village and power supply for household use and lighting in remote area, etc.
5) Agriculture Water pumping, agricultural products fumigator, thrashing machines and water sprayer, etc.
6) Cattle Water pumping, oxygen filling system for fish-farming and insect trapped lighting, etc.
7) Health center Refrigerator and cool box for keeping medicines and vaccines and medical equipment, etc.
8/) Communication Air navigational aid, air warning light, lighthouse, beacon navigation aid, illuminated road sign, railway crossing sign, street lighting and emergency telephone, etc.9) Telecommunication Microwave repeater station, telecommunication equipment, portable communication equipment (e.g. communication radio for service and military exercise) and weather monitoring station, etc.
10) Remote area Hill, island, forest and remote area that the utility grids are not available, etc. 11) Space Satellite, international space station and spacecraft, etc.
Warning: file_get_contents(domain/mp3play.online.txt): failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /www/wwwroot/link123456.online/getlink/index.php on line 27
play youtube
play youtube
xvideos
porn
xnxx
sex việt
Phim sex
Nba Score Schedule
Aus Racing Results
Florida Atlantic Basketball Schedule
Longines Classic Horse Race
Que Tiempored New York Yankees Hat
Cso Criminal Search Bc
Farfetch Coupon Code
Paul Ratiff
Your Earlobes Are Thick And Chewy
Cheap Miami Vacation Packages All Inclusive
How To Ruin A Car Without Evidence
Pga Tour Winner Predictions
Connect Google Mini
Cbb Espn Scores
Bookings Com Uk
What Did Mr Harvey Do To Susie
Fc Barcelona News Now
No Ceilings 3
Filed under: Understanding Solar Equipment

Leave a Reply